Isomerism in Coordination Compounds
Isomerism in Coordination Compounds: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Isomerism in Coordination Compounds, Stereoisomerism, Geometrical Isomerism, Geometrical Isomerism in Square Planar Complexes, Geometrical Isomerism in Octahedral Complexes, Facial Isomer, etc.
Important Questions on Isomerism in Coordination Compounds
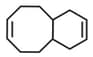
Number of geometrical isomer of given compound will be:
Among the following, a pair of resolvable configurational enantiomers is given by:
How many minimum no. of C-atoms are required for position and geometrical isomerism in alkene?
Which of the following compounds does exhibit stereoisomerism?
Which of the following has largest number of isomers?
(R is alkyl group, en is ethylediamine).
Which among the following compound does not has enantiomeric pair?
The isomerism exhibited by is
Geometrical isomerism is possible in?
An octahedral complex with molecular composition M.5NH3.Cl.SO4 has two isomers, A and B. The solution of A gives a white precipitate with AgNO3 solution and the solution of B gives white precipitate with BaCl2 solution .The type of isomerism exhibited by the complex is :
The total number of benzene derivatives having the molecular formula is
Which of the following complex does not show optical isomerism?
Which of the following complexes will show geometrical isomerism?
The spin only magnetic moment of complex of composition is . It can react with and shows geometrical isomerism. What is the name of the complex ?
Which of the following will give four isomers products (including the geometrical and optical isomerism)?
Number of stereoisomers possible for the octahedral complexes and respectively, are:
[-ethylenediamine]
A metal complex having composition , was isolated in two forms and ( is bromine and is iodine).
(a) reacts with and gives a pale yellow precipitate which is insoluble in .
(b) reacts with and gives a yellow precipitate which is insoluble in .
The octahedral complex exists in two isomeric forms and . Isomer reacts with to give a white precipitate, but does not react with . Isomer gives white precipitate with but does not react with
For an octahedral complex ( transition metal, and are monodentate achiral ligands), the correct statement among the following is
The complex that can exhibit linkage isomerism is
Indicate the complex ion which shows geometrical isomerism:
